3GPP described a new architectural model in Release 15, in which the gNB is split into three entities denoted as CU, DU and RRU as we have already seen in our previous post.
The RAN functions that correspond to each of the three entities are determined by the so called split points. After an analysis of the possible split options, 3GPP decided to concentrate on two split points: the split 2 and split 7, and only the former one was standardized by the end. The resulting partitioning of network functions is shown in Figure Below.
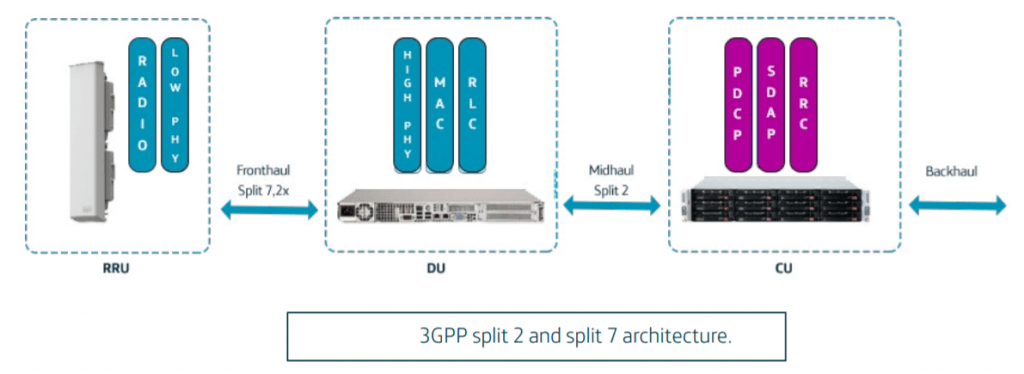
The CU (Centralized Unit) hosts the RAN functions above split 2; the DU (Distributed Unit) runs those below split 2 and above split 7; and the RRU hosts the functions below split 7 as well as all the RF processing.
The O-RAN Alliance further specified a multi-vendor fronthaul interface between the RRU and DU, by introducing a specific category of split 7 called split 7-2x, whose control, data, management, and synchronization planes are perfectly defined.
The midhaul interface between CU and DU can also be defined by 3GPP and further upgraded by the O-RAN Alliance to operate in multivendor situations. However, the actual advantage of this split design comes from the possibility to centralize the CU, and also the DU in some scenarios, in appropriate data centers where all RAN functions may be completely virtualized and running on suitable servers. The infrastructure needed to construct a DU is nothing else than a host based on Intel Architecture optimized to run those real-time RAN functions located below split two, and also to connect with the RRUs through a fronthaul interface based on O-RAN split 7-2x. It is the real time temperament of the DU that prompts the need to optimize the servers required to operate DU workloads.
Benefit from Massive discount on our 5G Training with 5WorldPro.com
Start your 5G journey and obtain 5G certification
contact us: contact@5GWorldPro.com


