According to protocols, the subcarrier spacing supported by flexible numerology is 15 kHz, 30 kHz, 60 kHz, 120 kHz, and 240 kHz.
The 240 kHz subcarrier spacing is used only for sending downlink
synchronization signals. The following table lists the subcarrier spacing supported by different frequency bands.
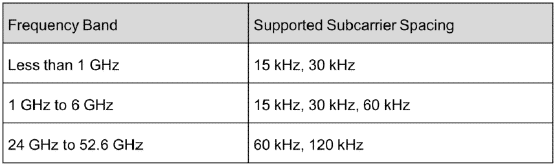
The higher the frequency band is, the larger the subcarrier spacing is supported.
Flexible numerology applies to the following scenarios:
- Delay: Different types of subcarrier spacing can be used for services with different delay requirements. A larger subcarrier spacing indicates a shorter slot, and the system delay can be shortened.
The uRLLC service can use smaller subcarrier spacing because of the lowlatency requirement.
- Mobility: The Doppler shift varies with the moving speed. A higher moving speed indicates a higher Doppler shift. By increasing the subcarrier spacing, the system can improve the robustness of the frequency offset.
The high speed train can use a large subcarrier spacing because of the Doppler shift.
- Coverage: A smaller subcarrier spacing indicates a larger CP length and a larger cell coverage radius.
Benefit from Massive discount on our 5G Training with 5WorldPro.com
Start your 5G journey and obtain 5G certification
contact us: contact@5GWorldPro.com


