Looking at how networks cover the world, most of the land (over 80%) and sea (95%) don’t get signals from regular ground cell networks. 5G, , was made to give fast internet and work everywhere. But in far-off places like mountains, deserts, and the ocean, it costs a lot to set up and keep a 5G network. So, these places can’t have 5G coverage. Thankfully, advances in space tech let satellites provide internet over big areas, without spending too much. This means 5G will mix with satellite tech to make a network that covers the whole planet, giving good service anywhere.
What is a Non-terrestrial network (NTN)?
Non-terrestrial Network (NTN) is a terminal-satellite direct communication technology based on the new radio (NR) interface technology developed by 3GPP in R17 and is also an important supplement to terrestrial cellular communication technology. With the integration of the satellite communication network and the ground 5G network, NTN can provide ubiquitous coverage without being restricted by terrain and landform, and connect the sky, earth, sea, and other spaces to form an integrated ubiquitous access network that enables on-demand access in all scenarios.
NTN is an important function of 3GPP R17. It continues to evolve in the 5G-Advanced stage and has become an important part of the 3GPP R18 work plan. NTN includes two workgroups: IoT NTN and NR NTN. IoT NTN focuses on satellite IoT services that support low-complexity eMTC and NB-IoT terminals, such as global asset tracking (sea containers or other terminals beyond the coverage of cellular networks). NR NTN uses the 5G NR framework to enable direct connection between satellites and smartphones to provide voice and data services.
Transparent NTN architecture
NTN consists of the user equipment (UE), satellite, satellite gateway, base station (gNB), core network (CN), and server. Its architecture will evolve from a more feasible transparent payload.
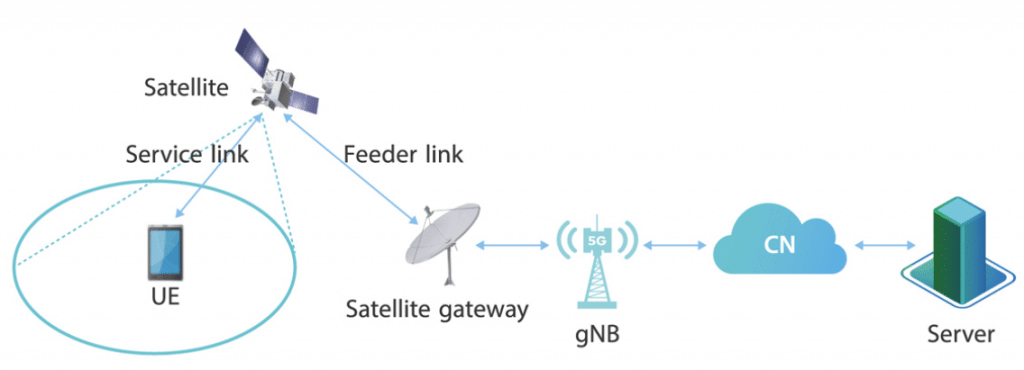
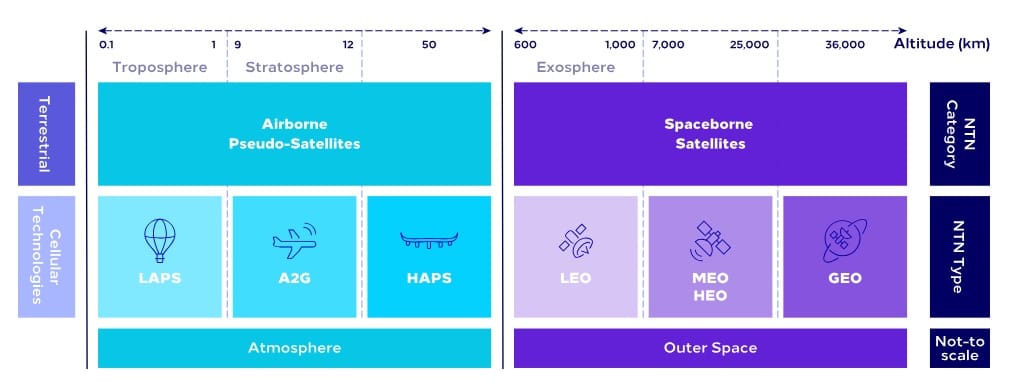
Next-generation wireless networks are envisioned to break the boundaries of the current terrestrial-based systems and fully adopt the Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTNs). NTN consists of variants of space-borne and aerial communication networks including GEO, MEO, LEO satellite constellations,High Altitude Platform Systems (HAPS), Low Altitude Platform Systems (LAPS), and air-to-ground (A2G) networks.
NTN elements and components are evolving to become an integral part of the future 6th Generation (6G) wireless network. NTN is growing in importance owing to its ability to offer “anything, anytime, anywhere” connectivity, thus connecting the unconnected
This NTN feature is only available in FDD operation due to the round-trip delay of the signal via satellite. In Rel-17, NTN is applicable in FR1 using S-band or L-band Devices that you hold, IoT devices, or VSAT terminals (which have antennas that point in a specific direction and higher transmission power) can be the ones connecting to NTN.
If a device wants to work with NTN, it needs to make up for the differences in time and frequency that happen because of the delay in the signal and the movement of the satellite during the time it takes for the signal to travel up to it. Additionally, the device must have the ability to figure out its position using GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) so that it can calculate the adjustments needed for time and frequency, along with where the satellite is and how it’s moving, based on the system information that’s sent out.
Don’t misse our 5G and Satellite Training to learn more about this NTN technology and how it related to 5G
Benefit from Massive discount on our 5G Training with 5WorldPro.com
Start your 5G journey and obtain 5G certification
contact us: contact@5GWorldPro.com


