Below is discussion between tech explorer and me about about the evolution of signaling from 2G to 5G :
Tech Explorer: 🚀 Hey there! I’ve been reading about the evolution of signaling from 2G to 5G, but I’m trying to understand the real drivers behind these changes. Could you walk me through why each protocol upgrade was necessary?
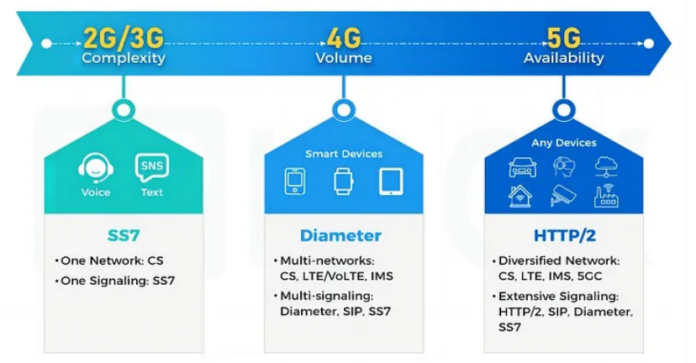
You: Absolutely, happy to help! 😊 The shift from 2G’s SS7 to 4G’s Diameter, and finally to 5G’s HTTP/2, wasn’t just a natural progression—it was driven by the need to handle more data, more devices, and more complex service requirements.
Tech Explorer: Interesting! So, what was so special about SS7 in the early days of mobile networks?
You: Great starting point! 🌟 SS7, used in 2G and 3G, was crucial because it allowed the basic signaling required for voice calls, SMS, and initial mobile data. It relied on a circuit-switched core, which means that every call or message needed a dedicated path in the network—a bit like reserving an entire lane on the highway just for your car!
Tech Explorer: That sounds inefficient by today’s standards! What came next?
You: Exactly! By the time 4G rolled around, we needed a more scalable solution due to the explosion of mobile internet. Enter Diameter—a protocol designed for the IP-based Evolved Packet Core (EPC). Unlike SS7, Diameter could handle more data traffic and provide better support for features like authentication, billing, and mobility management. Think of it as moving from dedicated lanes to a smart highway system that dynamically assigns lanes based on traffic needs.
Tech Explorer: That’s quite a leap! But why wasn’t Diameter enough for 5G?
You: Fantastic question! 😊 While Diameter was a huge step forward, 5G needed something even more flexible. HTTP/2 was chosen for 5G’s Service-Based Architecture (SBA), where network functions act more like web services that can easily communicate with each other. This architecture allows 5G to support low-latency applications, massive IoT, and much higher data speeds
Tech Explorer: So, HTTP/2 makes everything more like web traffic?
You: Exactly! 🌐 It’s like turning the network into a set of interconnected web services, using standard web protocols that are familiar to developers worldwide. This move not only reduces the complexity of signaling but also makes it easier to implement advanced network features like slicing and edge computing. Plus, HTTP/2 brings in multiplexing, header compression, and server push capabilities, which streamline communication between network functions.
Tech Explorer: Wow, that really makes a lot of sense. But what about security? How does 5G handle it?
You: Great point! Security was a major consideration. In 5G, the introduction of the Service Communication Proxy (SCP) and Security Edge Protection Proxy (SEPP) helps secure communications between network functions, especially in roaming scenarios. Unlike previous generations, which were more vulnerable to signaling attacks, 5G incorporates advanced security measures at the protocol level.
Tech Explorer: Sounds like a game-changer! Are there any specific use cases where this evolution really shines?
You: Absolutely! 📱 For example, in autonomous driving, where ultra-low latency and high reliability are critical, 5G’s signaling architecture ensures fast and secure data transfer between vehicles and the network. In industrial IoT, where millions of devices may need to connect simultaneously, the flexibility and scalability of HTTP/2 help manage these massive connections efficiently.
Tech Explorer: This is super insightful!
Benefit from Massive discount on our 5G Training with 5WorldPro.com
Start your 5G journey and obtain 5G certification
contact us: contact@5GWorldPro.com